
Portable Electrical Equipment Australian design Standards
Australian/New Zealand Standard™
Safety of household and similar electrical appliances
Part 1: General requirements (IEC 60335-1:1991, MOD)
The objective of this Standard is to provide manufacturers, designers, regulatory authorities,
testing laboratories and similar organizations with safety requirements designed to give the
user protection against hazards that might occur during normal operation and abnormal
operation of the appliance and which may be used as the basis for approval for sale or for
connection to the electricity supply mains in Australia and New Zealand.
7 Marking and instructions
7.1 Appliances shall be marked with the
– rated voltage or rated voltage range in volts;
– symbol for nature of supply, unless the rated frequency is marked;
– rated power input in watts or kilowatts or rated current in amperes;
– name, trade mark or identification mark of the manufacturer or responsible vendor;
– model or type reference;
– symbol for class II construction, for class II appliances only;
– IP number according to degree of protection against ingress of water, other than IPX0.
Appliances other than class III appliances intended for connection to the supply mains shall be marked with
– a rated voltage of at least:
230 V for single phase appliances;
400 V for polyphase appliances.
or
– a rated voltage range that includes:
230 V for single phase appliances;
400 V for polyphase appliances.
Compliance is checked by inspection.
NOTES
1 The first numeral of the IP number need not be marked on the appliance.
2 Additional markings are allowed provided they do not give rise to misunderstanding.
3 If components are marked separately, the marking of the appliance and that of the components is to be such that there can be no doubt with regard to the marking of the appliance itself.
Basic construction of electrical appliance to meet Australian electrical standards and regulations.
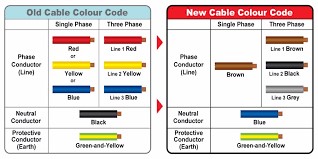
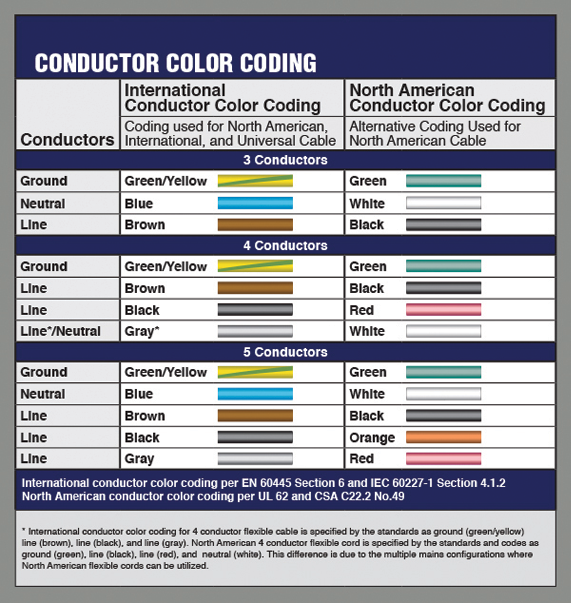
Mains input flex, 3 core for Class 1 (earthed) appliances, Brown insulation for active conductor, blue insulation for neutral conductor, green/yellow insulation for protective earth conductor.
Mains cable to be securely clamped where it enters the appliance for strain relief.
Mains cable to connect to a terminal block, clearly marked with connections A, N, E
Appliance to have a safety fuse or circuit breaker if a class 1 appliance.
Earth connection to case to be secure, can be screw or disconnect lug. Earth connection needs to be able to withstand 25 amp test current during Portable Appliance Test for Class 1 appliance. (protective earth as it is a Class 1 appliance)
Colour of insulation for wires going from circuit board to led board should not be brown, blue or green/yellow and show polarity. E.g. red positive and white common or red positive and black common.
Equipment label needs to show voltage, frequency, model name, serial number, manufacturer or supplier
Compliance Modifications to 36W LED Wash 8 December 2009-12-08
Earth needs to be securely connected to the case.
Can be by screw terminal. Earth lug such as a Utiliux disconnect spare or other suitable method. Suitable earth connection points for this fixture are on the end of the led pcb, on the side of the 3mm clamping screw, as has been done in this example, or by a utilux spade lug.
Earth contiunuity needs to be tested at 2.5 times the rating of the mains lead, normally done at 25 amps.
Colour of the earth wire is green/yellow, not red as in sample examined.
A fuse needs to be provided that does not allow any contact between the finger and any active contact.
A tool needs to be used to open up the fuseholder. (Desirable ?)
The active and neutral wires need to be secured by a terminal block unless an IEC inlet is used, as strain relief. In the sample the active and neutral wires were soldered onto the pcb, not though a hole, so the wires and copper track could have been pulled off the pcb and then make contact with the metal case.
The mains cable needs to be secured where it enters the chassis in some form of strain relief. A cable gland has been used in this example. The cable gland, a H4304 from Altronics has a PG7 thread so the end of the fixture has been tapped with a PG7 tap to secure the cable gland. Due to the limited space available, the cable gland has also been hot glued to secure the thread.
A safety M205 screw type fuseholder from Altronics, S5992, has been fitted into the end of the fitting. As there is not enough clearance for the fuseholder nut, the nut has been cut, then hot glued into plase.
At present, no fuse is fitted as the pcb does not have any insulating material between it and the aluminium channel.
A label needs to be fixed onto the fixture showing, input voltage, frequency of operation, serial number and model.
Contact details of the manufacturer or supplier may also be needed.
I will now convert the above to electrical regulations and Australian Standards.
References:
Requirements for importing electrical appliances and equipment – WA Energy Safety – http://www.commerce.wa.gov.au/EnergySafety/PDF/Publications/Information_E019_030.pdf
Electrical items that are not prescribed.
Persons who sell or hire electrical appliances or equipment which are not prescribed are responsible under the Common Law for ensuring the items are safe to be connected to electricity supply. Assurance may be achieved by obtaining a test report from an independant testing laboratory, confirming compliance with the relevant Australian/New Zealand Standards for electrical safety. This report can then be provided, if requested to a prospective buyer, to show compliance.
The 36w beamlight is not on the list of prescribed appliances.
Electricity Act 1945 Western Australia – Part IVA – Approval of electrical appliances – http://www.slp.wa.gov.au/pco/prod/FileStore.nsf/Documents/MRDocument:15489P/$FILE/ElecityAct1945_07-b0-03.pdf?OpenElement
33B Power of Director to prescribe classes or types of electrical apparatus etc, which shall not be sold etc, unless approved by the Director.
The 36w beamlight is not on the list of prescribed appliances.
Safety of Electrical Appliances – How to obtain approval to sell electrical appliances in Western Australia – http://www.commerce.wa.gov.au/energysafety/PDF/Factsheets/safety_electrical_ap.pdf
Includes a List of Prescribed Electrical Appliances.
The 36w beamlight is not on the list of prescribed appliances.
Electrical compliance standards – Electrical Solutions – list of electrical compliance standards – http://www.electricalsolutions.net.au/contents/1429-Electrical-compliance-standards refers to Electrical compliance Standards:
AS/NZS3820:1998 Essential safety requirements for low voltage electrical equipment
AS/NZS3350.1:2000 Safety of household and similar electrical appliances.
AS/NZS 3820:1998 Essential safety requirements for low voltage electrical equipment
- SAFETY REQUIREMENTS
4.1 General Conditions
Electrical equipment shall comply with the following criteria:
The essential characteristics, the recognition and observance of which will enable electrical equipment to be used safely and in applications for which it was made, shall be marked in English on the equipment, or if this is not possible, on an accompanying notice. Such characteristics shall include the rated voltage and frequency.
The conductors of single phase flexible cords would be required to be uniquely and correctly identified throught their length by colour of the insulation of the conductors. Green, yellow and green/yellow combinations are only to be used to identify the earth-continuity conductor.
Where the connection pointof an electrical appliance is able to be replaced by other than the manufacturer, then the appliance terminals wouls need to be clearly identified in accordance with AS/NZS 3350.1
AS/NZS 4417.2:2001 Marking of electrical appliances to indicate compliance with regulations.
Part 2: Specific requirements for electrical safety regulatory applications.
AS/NZS 3128:1998 Approval and test specification – Portable lamp standards and brackets
AS/NZS 60598.2.4:2005 Luminaires Part 2.4: Particular requirements – Portable general purpose luminaires
Page updated 17 August 2020